
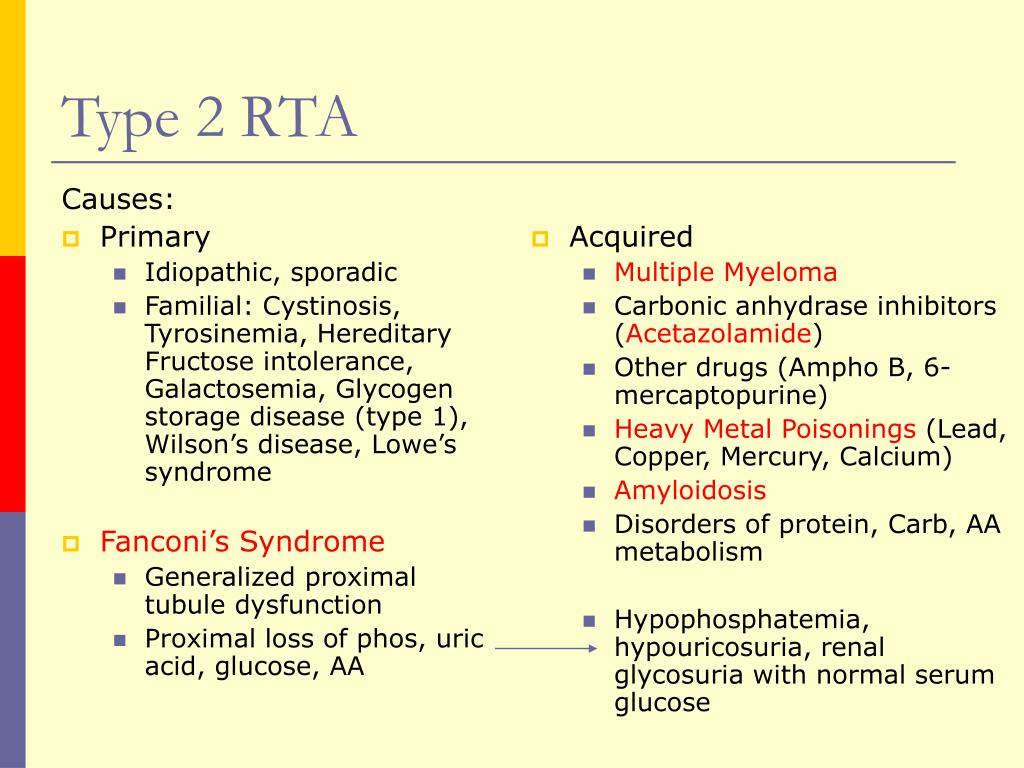
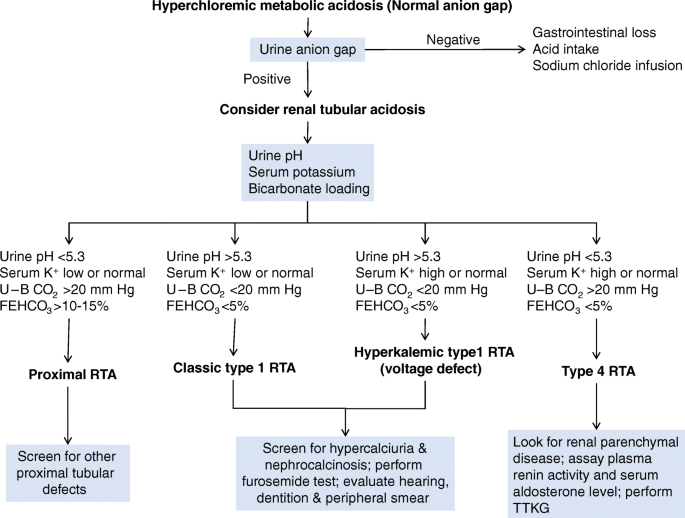
A positive gap in setting of metabolic acidosis suggests an RTA.Īll figures included created by Joel Topf MD and reproduced with his permission. Remember: a “neg-GUT-ive” gap means ammonium is present and effective renal acid secretion is intact.
Urine anion gap: Indirectly measures ammonium (NH4+). One teaspoon of baking soda has 60 mmol bicarb Bicarbonate pills come in 650 mg (8 mmol bicarb) or 325 mg (4 mmol bicarb). Note: 1 mEq/L = 1 mmol/L for bicarbonate. Bicarbonate repletion: Treat to serum bicarb > 22. Type 4 RTA (hypoaldosteronism): Chronic hyperkalemia impairs ammoniagenesis. Treatment: Bicarbonate +/- potassium replacement Complications: Hypo- or hyperkalemia (depending on defect) Osteoporosis Nephrolithiasis (worse on treatment). Distal Type 1 RTA: Failure of H+ secretion in distal nephron with multiple mechanisms. Complications: Osteoporosis Nephrolithiasis and hypokalemia occur if bicarbonate (alkali) therapy given due to bicarbonaturia. Serum bicarbonate drops to new “set point”. Proximal renal tubular acidosis (Type 2 RTA): Damage to proximal tubule impairs bicarbonate reabsorption. Using “balanced” solution like ringer’s lactate instead of saline reduced major adverse kidney events by 1% in the SMART and SALTED trials NEJM 2018. Normal saline creates a non anion gap metabolic acidosis (NAGMA) due to chloride 154 mEq/L. Non gap metabolic acidosis: GI losses are the most common cause so “don’t go looking for the zebra of RTA”. Hosts: Matthew Watto MD, Stuart Brigham MD, Paul Williams MD Written by: Matthew Watto MD and Joel Topf MD 
Rate us on iTunes, recommend a guest or topic and give feedback at.
#Rta type pdf#
Join our mailing list and receive a PDF copy of our show notes every Monday. You may want to go back and check out episode #88 Acid Base, Boy Bands and Grandfather Clocks with Joel Topf MD if you haven’t heard it yet. Check out Dr Topf’s awesome slides on renal tubular acidosis at. We review the three buckets of non gap metabolic acidosis, normal renal physiology & acid base handling, points of failure in RTA, complications and treatment of RTA. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.Renal tubular acidosis aka RTA deconstructed by Joel Topf MD, Chief of Nephrology at Kashlak Memorial Hospital. Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M.
Use of certain medicines, such as amphotericin B, lithium, and analgesicsĪ.D.A.M., Inc. Wilson disease, an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. Systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Sjögren syndrome, an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. Sickle cell disease, red blood cells that are normally shaped like a disk take on a sickle or crescent shape. Fabry disease, an abnormal buildup in the body of a certain type of fatty substance. Amyloidosis, a buildup of abnormal protein, called amyloid, in the tissues and organs. Type I RTA is caused by a variety of conditions, including: The kidneys help control the body's acid level by removing acid from the blood and excreting it into the urine.ĭistal renal tubular acidosis (type I RTA) is caused by a defect in the kidney tubes that causes acid to build up in the blood. It can also cause problems with normal function of some cells. This can lead to electrolyte imbalances in the blood. 
If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood becomes too acidic. When the body performs its normal functions, it produces acid.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
